Sentiment Analysis and Opinion Mining
A significant portion of news and social media coverage contains opinions with clear economic relevance. Product and travel reviews or the articles of well-known bloggers, for example, influence consumer purchase decisions. Sentiment analysis and other opinion mining techniques to process this user-generated content are therefore becoming imperative for decision makers who aim to engage with large user communities.
Turning Data into Opinions
The ever-increasing amount of such user-generated content and the limits of human cognition require automated approaches to analyzing the sentiment expressed in online content. As part of opinion mining, sentiment analysis identifies and aggregates polar opinions – i.e., positive or negative statements about facts.
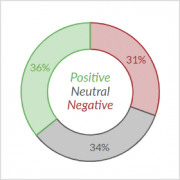
webLyzard provides the results of this automated classification as data services or visual tools. Color-coding indicates the assigned class. As shown below, colors range from red (negative) to grey (neutral) and green (positive). They vary in saturation, depending on the degree of polarity. Vivid colors hint at emotionally charged issues, while less saturated ones reflect a more neutral coverage.
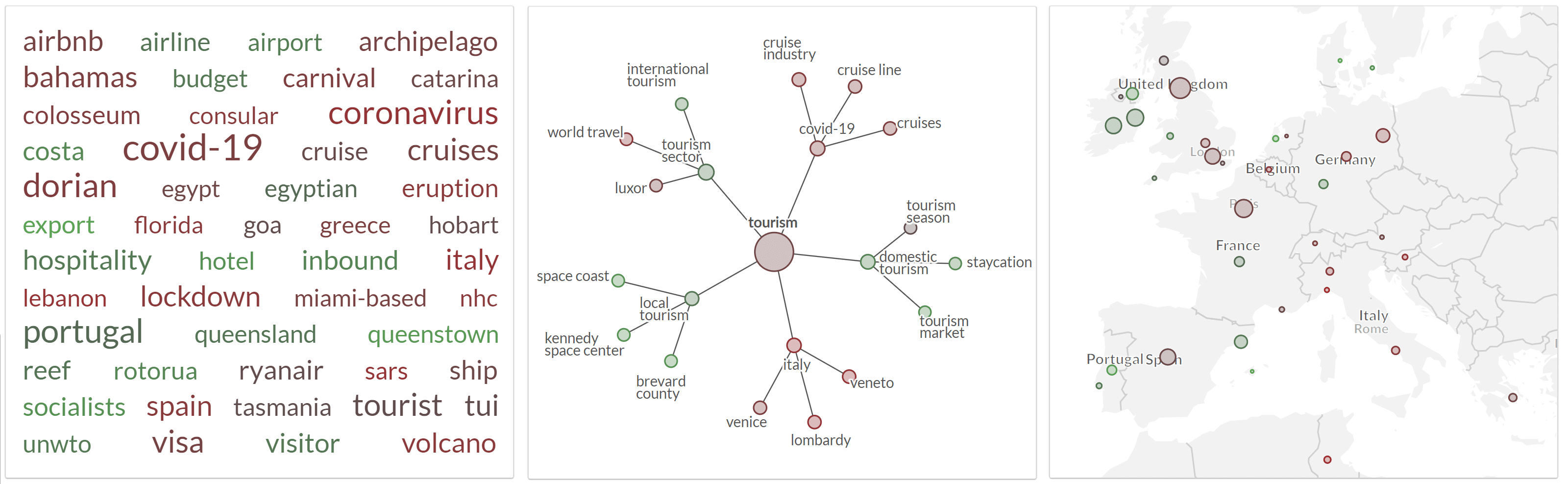
Visual tools including tag cloud, keyword graph and geographic map. The sentiment for the search term “tourism” reflects the impact of the coronavirus pandemic.
Multilingual Sentiment Analysis
Parlez-vous français? User-generated content from social media platforms is noisy, unstructured, and multilingual. Extracting opinions from this type of content therefore requires robust text mining techniques. Use cases range from simple spelling corrections to more complex tasks such as sentiment analysis or the identifying entities (locations, persons, organizations).
 Given that more and more users communicate in global information networks, multilingual capabilities are becoming increasingly important. As a first step, the system needs to detect the language(s) used. This is a comparably straightforward task. We then need specific language resources, for example sentiment lexicons. Without doubt the most challenging is the correct parsing of grammatical structures. Unusual expressions in specific language communities further complicate this process.
Given that more and more users communicate in global information networks, multilingual capabilities are becoming increasingly important. As a first step, the system needs to detect the language(s) used. This is a comparably straightforward task. We then need specific language resources, for example sentiment lexicons. Without doubt the most challenging is the correct parsing of grammatical structures. Unusual expressions in specific language communities further complicate this process.
Dealing with Ambiguity
Is it Apple or an apple? Does the tweet refer to the multinational technology company or an edible fruit? Many automated systems cannot resolve such ambiguities. webLyzard addresses this problem not only through context awareness and domain-specific knowledge, but also through its ability to identify relations between semantic concepts.
 Recent articles published in Knowledge-Based Systems and IEEE Intelligent Systems present our novel approach to contextualization. They describe the development of the underlying methods. They also outline advantages over existing approaches, based on detailed evaluations. User reviews of movies (IMDb), hotels (TripAdvisor) and products (Amazon) provided the gold standard for these evaluations.
Recent articles published in Knowledge-Based Systems and IEEE Intelligent Systems present our novel approach to contextualization. They describe the development of the underlying methods. They also outline advantages over existing approaches, based on detailed evaluations. User reviews of movies (IMDb), hotels (TripAdvisor) and products (Amazon) provided the gold standard for these evaluations.
The first 2013 IEEE article focuses on disambiguation and the generation of contextualized sentiment lexicons. The second article in Knowledge-Based Systems extends this method. It uses knowledge graph enrichment techniques to integrate external affective resources into the opinion mining process. The third 2017 IEEE article then increases the granularity by focusing on specific aspects. This includes product features (e.g., a digital camera’s resolution) or specific events (e.g., as part of a sponsorship agreement). Another important extension is emotion detection. In contrast to the bipolar sentiment model, emotion extraction uses more fine-grained affect models to distinguish human emotions such as Joy, Trust, Anger and Fear.
Sentiment Analysis References
- Weichselbraun, A., Gindl, S., Fischer, F., Vakulenko, S. and Scharl, A. (2017). “Aspect-Based Extraction and Analysis of Affective Knowledge from Social Media Streams“, IEEE Intelligent Systems, 32(3): 80-88.
- Weichselbraun, A., Gindl, S. and Scharl, A. (2014). “Enriching Semantic Knowledge Bases for Opinion Mining in Big Data Applications”, Knowledge-Based Systems, 69:78-85.
- Weichselbraun, A., Gindl, S. and Scharl, A. (2013). “Extracting and Grounding Contextualized Sentiment Lexicons”, IEEE Intelligent Systems, 28(2): 39-46.
- Scharl, A. and Weichselbraun, A. (2008). “An Automated Approach to Investigating the Online Media Coverage of US Presidential Elections”, Journal of Information Technology & Politics, 5(1): 121-132.